This post is also available in:
ไทย (Thai)
For many well-meaning and talented innovation leaders, managing innovation can feel like wrestling with chaos. It’s a world of promising but scattered pilot projects, sudden budget cuts, resistance to change, and constant pressure from leadership to deliver measurable results from an unpredictable process. But what if there was a way to bring order to this chaos? What if you had a playbook, recognized globally, to transform innovation from a series of random, high-risk activities into a structured, manageable, and value-creating business function?
That playbook exists. It’s called ISO 56001: Innovation Management System.
This comprehensive guide is designed for innovation leaders like you. It will walk you through what an Innovation Management System (IMS) is, how the ISO 56001 standard provides the ultimate framework, and how you can use it to build a powerful, controllable engine for sustainable growth within your organization.
Table of Contents
- What is an Innovation Management System (IMS)?
- The ISO 56000 Family: A Common Language for Innovation
- Deep Dive: The Core Components of the ISO 56001 Playbook
- The Philosophy Behind the Process
- The Strategic Advantage: Why an IMS is More Than a Certificate
- Your First Move: Starting the Journey
1. What is an Innovation Management System (IMS)?
An Innovation Management System (IMS) is a set of interrelated and interacting elements within an organization that establish innovation policies, objectives, and processes to achieve those objectives.
Think of it like the operating system (OS) for innovation. Just as a computer’s OS manages all its hardware and software so you can perform complex tasks, an IMS manages all your company’s resources, processes, and strategies so you can deliver innovation effectively and repeatedly. A powerful example of a systematic approach delivering tangible results comes from Swiss Post. By implementing a structured campaign focused on incremental process improvements from employees, the company was able to unlock over $2 million in “quick win” savings and efficiencies. This demonstrates how an IMS can turn small, distributed ideas into significant, measurable value.
Swiss Post leveraged its long-standing partnership with Qmarkets to launch a nationwide Kaizen-driven improvement campaign, achieving over $2.4 million in savings within weeks. By repurposing the Qmarkets platform, 130 internal Kaizen experts conducted audits across 73 logistics sites, identifying over 600 actionable improvements. This bottom-up approach empowered employees to lead change, fostering rapid execution and cross-site learning.
The initiative, called Kaizenfluencer, showcased Swiss Post’s decentralized innovation model—where local teams drive ideas while a central unit ensures strategic alignment. This structure enabled fast, scalable improvements without hiring consultants or building new systems. The campaign also strengthened trust and engagement, with peer-to-peer reviews enhancing transparency and motivation.
In 2024, Swiss Post expanded its Kaizen efforts, submitting nearly 5,000 ideas and reclaiming 100,000 work hours, resulting in an additional $3.2 million in savings.
The success highlights key lessons for innovation leaders: repurpose existing tools creatively, balance autonomy with structure, and prioritize small wins for big impact.
An IMS moves innovation from a reactive, project-by-project process to a predictable and enduring organizational capability.
The goal of an IMS is to address the most common failures in corporate innovation: lack of strategic alignment, inconsistent processes, insufficient resources, and an inability to scale new ideas.
2. The ISO 56000 Family: A Common Language for Innovation
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) created a series of standards—the ISO 56000 family—to provide a globally recognized and authoritative framework for managing innovation. While there are several documents in the series, these are the most critical to understand:
- ISO 56000: Fundamentals and Vocabulary: The starting point. It defines the core terms and the eight essential principles of innovation management.
- ISO 56002: Guidance: This is a detailed guide with suggestions on how to implement an IMS. It provides the “shoulds.”
- ISO 56001: Requirements: This is the heart of the system. It is the only standard in the series that contains the formal requirements for an IMS against which an organization can be audited and certified. It provides the “shalls.”
3. Deep Dive: The Core Components of the ISO 56001 Playbook
ISO 56001 is built on the same High-Level Structure (HLS) as other major ISO standards like ISO 9001 (Quality). This makes it easy to integrate into existing management systems. It follows the classic Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle.
For leaders familiar with quality management, understanding how the innovative, exploratory cycle of ISO 56001 complements the stable, process-driven cycle of ISO 9001 is a critical first step. Read our complete guide comparing ISO 56001 vs. ISO 9001 here.
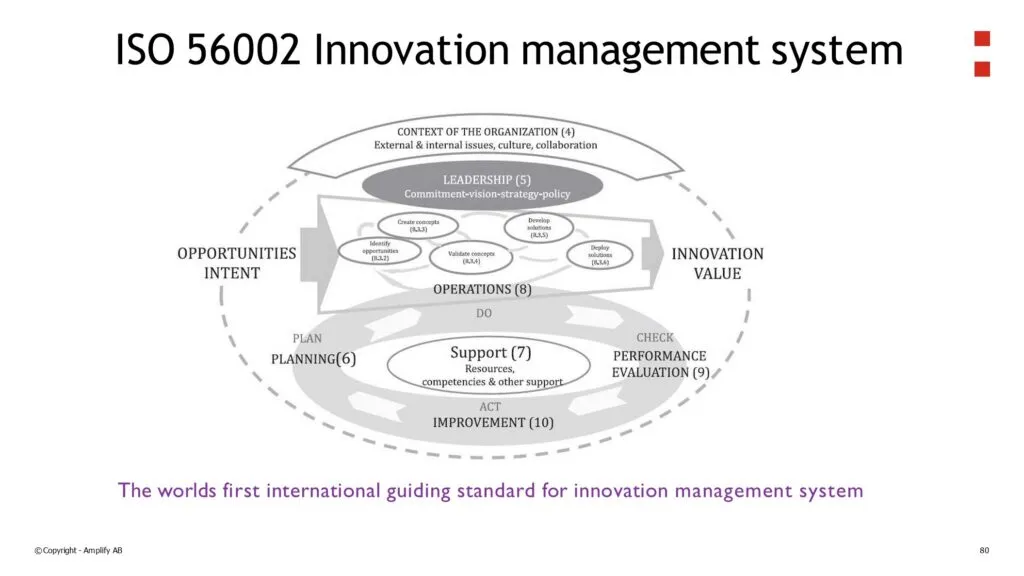
PLAN: Setting the Direction (Clauses 4, 5, 6, 7)
This is where you build the foundation and business case for innovation, secure leadership commitment, and plan for risks and resources.
DO: Executing the Plays (Clause 8)
This is the operational heart of your playbook. It covers the processes for the entire innovation journey, from identifying opportunities to deploying solutions.
CHECK: Measuring Performance (Clause 9)
This clause requires you to decide what you will measure and how you will evaluate the performance of your IMS. This directly addresses the ‘ROI Squeeze’ by giving you a system to track and report on innovation performance.
This ability to track performance is the foundation for getting executive buy-in. To learn how to translate these performance metrics into a compelling financial argument, see our complete framework for building a business case and proving ROI to your C-Suite.
ACT: Driving Continuous Improvement (Clause 10)
An IMS is not a static project; it’s a living system. This clause requires you to continually improve the effectiveness of the IMS, learning from both successes and failures.
4. The Philosophy Behind the Process
Beyond the clauses and requirements, a truly successful implementation is guided by a deeper philosophy. The entire standard is built upon eight core principles—from fostering a supportive culture to the role of future-focused leadership. Understanding this “spirit” of the standard is what separates a compliant system from a game-changing one. Explore the 8 Core Principles of Innovation Management in our foundational guide.
5. The Strategic Advantage: Why an IMS is More Than a Certificate
Implementing an ISO 56001-compliant IMS provides benefits that go far beyond a certificate on the wall. It gives you, the innovation leader, the structure and legitimacy to succeed.
6. Your First Move: Starting the Journey
Understanding the theory of ISO 56001 is the first step. The next is to understand where your organization stands today. Most organizations begin their journey by conducting a gap analysis or an innovation maturity assessment to benchmark their current processes against the requirements of the standard. This will give you a clear action plan.
